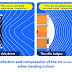
Ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging tool that uses high-frequency sound waves to detect changes inside your body. These waves travel through your body and hit the boundary between your tissues. Some of them reflect back to the probe while others travel onto the next boundary. These waves are picked up by the ultrasound probe and sent to the ultrasound machine for analysis. The machine calculates distances between tissues by using the speed of sound within the tissue, which is about 5,005 feet per second, and the time it takes for the sound to re-echo.
Transducer probes
Ultrasound machines use transducer probes to produce images of the body. They are the most important tool in the process. When choosing a probe, you should consider the type of procedure you will be performing and the types of exams you will be performing. In the next part of this article, we will discuss how transducers are oriented and what the different views of ultrasound are.
An ultrasound transducer is made of piezoelectric materials that respond to an electrical field by changing shape and generating electrical potentials. The polarity of the voltage applied to the transducer will change the thickness of the transducer and produce mechanical pressure waves. Echoes created by this effect cause small potentials across the transducer.
Field of view
A field of view (FOV) is a term that describes the largest diameter of a reconstructed image. It can be changed by the operator and typically ranges from 12 to 50 centimeters. A large FOV means that the reconstructed image will include the whole region of interest, while a small FOV means that some of the areas of interest may be excluded. In both cases, the FOV can be changed in the machine's settings or by changing the raw image data.
A secondary control on an ultrasound machine is its gain knob. It is an easy way to adjust the overall brightness of the image and it can dramatically affect the image quality. Most ultrasounds have a gain knob, and it is recommended to get into the habit of adjusting it after each scan. Even a slight twist can make a big difference in the image quality.
Resolution
One of the key factors in determining how well an ultrasound machine works is its resolution. This is the ability of the ultrasound system to detect small objects in both axial and lateral directions. Axial resolution is a measure of the sharpness of the image. A narrow beam width with a high frequency gives good lateral resolution. A wide beam with a low frequency has poor lateral resolution.
An ultrasound machine's resolution is essential for observing objects in motion. The human eye requires an image update rate of 25 frames per second, so an ultrasound machine's resolution should be high enough to capture the smallest movements. The frame rate should be optimized to maximize image quality. Ultrasound resolution can be affected by the boundaries of an ultrasound field, which causes part of the ultrasound to be reflected and transmitted. The angle of reflection and transmission is also an important factor when determining the resolution of an ultrasound image.
Doppler technology
Using Doppler technology is a good way to measure blood flow in your body. The Doppler spectrum of blood flow contains information about cardiovascular health. The signal consists of single-frequency signals from scatterers with varying velocities. Each of these signals has a specific frequency, amplitude, and phase. The signal processing required is straightforward. After receiving the signal, high-pass filters are used to eliminate low-frequency Doppler signals. The frequency components are then analyzed to compute the power spectrum.
There are many different kinds of ultrasound equipment. Some are used for specialized diagnostic purposes, while others are used as part of a routine procedure. The type of ultrasound equipment you use will depend on the type of procedure you're performing.
| Similar Content |
|---|
| What is an Ultrasound Machine Used For? |
| 5 Uses of Ultrasound |
| What Can an Ultrasound Test Detect? |
| How Does a Basic Ultrasound Work? |