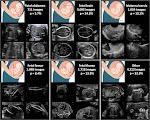
An ultrasound machine is a medical device that produces images of the human body. Its capabilities can vary, depending on the type of ultrasound you need. Some are general and can perform a wide range of procedures, while others are more specialized. A standard ultrasound has a series of general features, but some specialised ultrasounds require a specific set of options. These options include probes, also known as transducers, and software.
Transducer probe
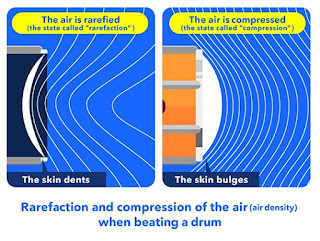
The ultrasound machine's transducer probe produces the ultrasound images that are visible on the monitor. It is called a transducer because it produces a series of parallel ultrasound waves. This allows the machine to provide a similar resolution in both near-field and far-field imaging. The transducer is used for imaging musculoskeletal structures, specific blood vessels, and in ultrasound-guided procedures. It also helps to measure blood flow and the speed of sound in the blood.
The transducer is the most important tool used in ultrasound. It is important to select the right transducer based on what type of exams and procedures you will perform with it. Here are some basic principles for transducer positioning:
Class II
A Class II ultrasound machine meets FDA performance standards for use in the medical field. This type of ultrasound machine emits ultrasonic waves. The FDA has developed performance standards for this type of ultrasound equipment, which are based on the Radiation Control for Health and Safety Act. Class II ultrasound machines include various types of imaging transducers for external and internal use. Some models are also equipped with intravascular ultrasound catheters for imaging coronary arteries.
The FDA does not require pre-market approval for class II ultrasound machines, but requires that these products meet certain statutory standards before they can enter the market. While they are exempt from pre-market approval, class II devices are still subject to strict quality control and manufacturing standards. These machines must be evaluated by a qualified radiologist before they can be sold.
| Similar Content |
|---|
| 5 Uses of Ultrasound |
| What Can an Ultrasound Test Detect? |
| How Does a Basic Ultrasound Work? |
| How Is Your Ultrasound Machine Working? Part 2 |